🌦️ WeDeAn – Weather Derivatives Analyzer
WeDeAn (Weather Derivatives Analyzer) is a Python and Streamlit-based application for analyzing weather data and valuing HDD/CDD-based weather derivatives. It integrates DWD (Deutscher Wetterdienst) datasets, computes degree-day indices, and applies burn analysis to estimate the theoretical payoffs and fair values of weather options.
👉 Check out on GitHub
🚀 Features
-
Load and process DWD weather datasets: Automatically reads and cleans station data (e.g., TMK, RSK, SDK) and prepares it for analysis.
-
Calculate Heating and Cooling Degree Days: Converts daily temperature data, the core indices used in weather derivatives.
-
Adjust for climatic trends: Optionally detrend long-term CDD/HDD series to remove warming or cooling biases.
-
Burn analysis pricing: Calculates historical payoffs and fair values of HDD/CDD-based options using actual observed weather.
-
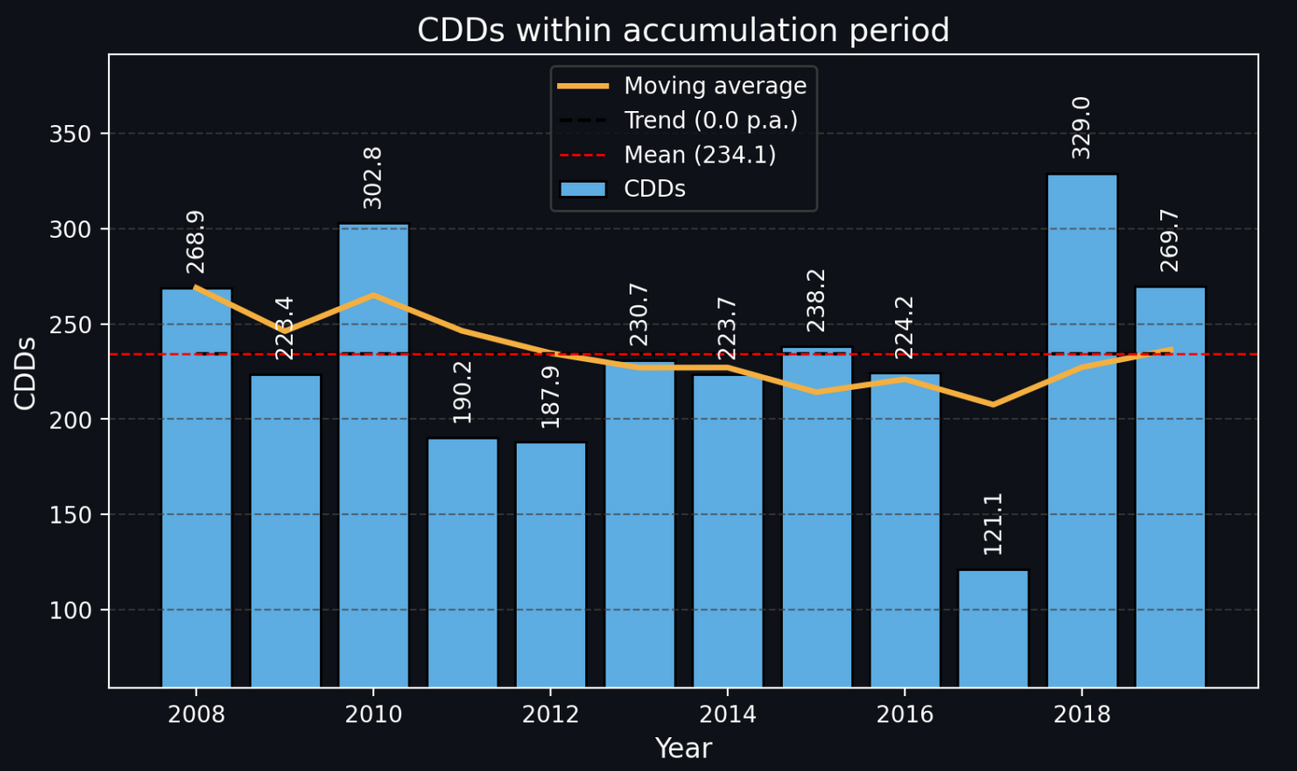
Interactive visualizations: Displays time-series plots, rolling averages, payoff curves, and fair value results - fully integrated in a Streamlit dashboard.
📊 High-Level Process
- Load Dataset – Select a weather station and import its historical data (TMK, SDK, RSK, etc.).
- Clean & Filter – Restrict data to a selected observation window (
Observation length) and remove years with incomplete data. - Compute Degree-Day Indices – Aggregate daily HDDs/CDDs into seasonal accumulated values.
- Trend Adjustment (optional) – Remove long-term temperature trends.
- Calculate Payoffs – Compute annual option payoffs from accumulated indices.
- Price Options (Burn Analysis) – Estimate fair values as the discounted historical mean of those payoffs.
🧮 Core Concepts
HDDs (Heating Degree Days)
A measure of how much and for how long the outside air temperature is below a base temperature (commonly 18°C). Used to estimate heating demand - colder weather means higher HDDs and greater energy use.
Formula:
HDD_i = max(0, T_base – T_i)
CDDs (Cooling Degree Days)
A measure of how much and for how long the outside air temperature is above a base temperature (commonly 18°C). Used to estimate cooling demand - hotter weather means higher CDDs and more electricity use.
Formula:
CDD_i = max(0, T_i – T_base)
Fair Value of CDD/HDD Options
The expected (average) payout, discounted to present value.
Can be estimated by:
- Historical simulation (burn analysis)
- Statistical modeling
- Monte Carlo simulation
Pricing Using Burn Analysis
A transparent pricing method using historical weather records.
- Compute the HDD/CDD index for each historical year.
- Calculate the option payoff (e.g., call/put) for each burn year.
- Take the average discounted payoff across all years as the fair value.
Assumption: Past temperature distributions represent the future (unless trend-adjusted).
▶️ Run the Application
1. Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/trholy/wedean.git
cd wedean
2. Build and run docker container
docker-compose up --build
3. Open in your browser: The app will launch at http://localhost:8501
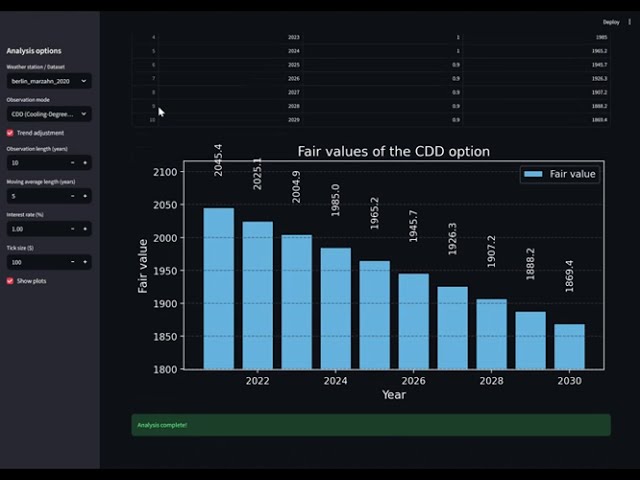
Example Output
- Berlin Marzahn 2020
- CDDs
- Trend adjusted
- Observation length: 12 years
- Moving average length: 5 years
- Interest rate: 2.0%
- Tick size 100$

📂 Project Structure
├── .dockerignore
├── .gitignore
├── Dockerfile
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── datasets
├── docker-compose.yml
├── pyproject.toml
├── setup.py
├── src
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── wedean
│ │ ├── calculation
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── calculation.py
│ │ ├── data_handling
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── data_handling.py
│ │ ├── plotting
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── plotting.py
│ │ └── utils
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── utils.py
└── streamlit-app
├── app.py
├── requirements.txt
└── utils.py
📜 License
This project is released under the MIT License. You are free to use, modify, and distribute it with attribution.